| Framework for knowledge management |
 |
|
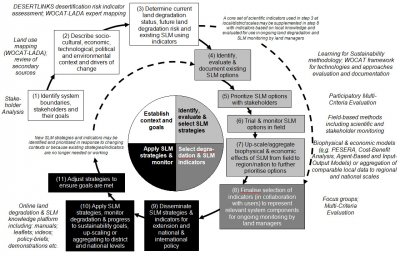
For land degradation monitoring and assessment (M&A) to be accurate and for sustainable land management (SLM) to be effective, it is necessary to incorporate multiple knowledges using a variety of methods and scales, and this must include the (potentially conflicting) perspectives of those who use the land. This paper presents a hybrid methodological framework that builds on approaches developed by UN Food & Agriculture Organisation’s land degradation Assessment in Drylands (LADA), the World Conservation Approaches and Technologies (WOCAT) programme and the Dryland Development Paradigm (DDP), and is being applied internationally through the EU-funded DESIRE project. The framework suggests that M&A should determine the progress of SLM towards meeting sustainability goals, with results continually and iteratively enhancing SLM decisions.
This approach incorporates multiple knowledge sources and types (including land manager perspectives) from local to national and international scales. In doing so, it aims to provide outputs for policy-makers and land managers that have the potential to enhance the sustainability of land management in drylands, from the field scale to the region, and to national and international levels. The paper draws on operational experience from across the DESIRE project to break the four themes into a series of methodological steps, and provides examples of the range of tools and methods that can be used to operationalise each of these steps.
This report is adapted from the following paper: Reed MS, Buenemann, M, Atlhopheng J, Akhtar-Schuster M, Bachmann F, Bastin G, Bigas H, Chanda R, Dougill AJ, Essahli W, Evely AC, Fleskens L, Geeson N, Glass JH, Hessel R, Holden J, Ioris A, Kruger B, Liniger HP, Mphinyane W, Nainggolan D, Perkins J, Raymond CM, Ritsema CJ, Schwilch G, Sebego R, Seely M, Stringer LC, Thomas R, Twomlow S, Verzandvoort S (2011) Cross-scale monitoring and assessment of land degradation and sustainable land management: a methodological framework for knowledge management. Land Degradation & Development 22: 261-271. An earlier version of the report was originally published as part of the Dryland Science for Development Consortium’s Working Group 3, presented at the first UNCCD CST Scientific Conference at COP-9, 22-24 September 2009 in Buenos Aires, Argentina
|
|||||||||

Acknowledgement
The DESIRE project was
|
DESIRE brought together the expertise of
26 international research institutes
and non-governmental organisations.
This website does not necessarily
represent the opinion of the
European Commission. The European
Commission is not responsible for
any use that might be made of the
information contained herein.