Conservation measures and experimental setup
Experimental set up
- Plots of 300 m2 (30 * 10 m), are delimitated by small earth wall and a H-flume downstream conduce runoff and sediments eroded to tanks of 100 l capacity. In case of higher runoff volume, a nearly 2% of water quantity is retain in a second tank. Water with sediments were sampled after every events (means nearly every day during rainy season).
- The plots are under 4 different agronomical treatments based on the traditional crop association of maize without association and fallow: Fallow, traditional crop, zero tillage+crop residues, crop with improved fertility (chemical + crop residues). In year 4 and 5 the improved fertility treatment had been replaced by barley crop. Ploughing direction is normal.
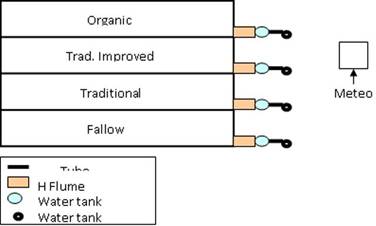
Soil erosion measurement plots (10 * 30 m)
|
H-Flume and water tanks filled |
Climatic station (Photos: Prat, 2007) |
Land preparation with tractor |
Land preparation with yoke of oxen (Photo: Prat, 2005) |
|
Plot with emerging corn |
Barley ready to be collect (Photo: Prat, 2007) |
Plot with barley. |
Tensiometers in the plots during the dry season (photo: C. Prat 2007) |
Expected effects
Impact of mulching, reduced soil working and crop residues must increase the soil fertility and so the production of the crop for man and animal uses, infiltration rate (so reduction of runoff and soil erosion) as well on C capture through reduction of compaction, splash erosion and crusting as well increasing of soil life activities.







