|
Identifying strategies: Stakeholder Workshop 1 |
 |
|
A report on the results of the workshop "Land degradation and desertification - existing and potential prevention and mitigation strategies" held in Sehoul, Morocco from 19-21 June 2007
|
Field work and workshops on "existing and potential mitigation strategies against land degradation" were conducted with the objectives of sharing experience on current and potential problems and solutions regarding land degradation and desertification.
The aims are:
- to identify existing and new strategies to prevent or mitigate land degradation and desertification.
- to select a set of these identified strategies for further evaluation and documentation with the WOCAT methodology
- to experiment with these strategies in some fields and make a follow-up with some required techniques of measurement.
The overall objective is to be able, after some years of experimentation to propose successful strategies for extension and improvement. The field work programmed is the monitoring of these techniques and approaches in order to determine their efficiency, both in terms of land degradation mitigation, social benefits and farm yield increase.
|
Main problems of degradation in the region
 |
1. Inside the forest, the poor social situation of the population explains the rapid retreat and clearing of the vegetation cover, the non-regeneration of cork oak and the multiplication of poor species.
|
 |
2. In the pastures, located on steep slopes, over-grazing leads to the degradation of the vegetation cover to the reduction of palatable species and to the development of rills and gullies.
|
|
3. In the cultivated area, the problems are more related to techniques of land use that are not adapted to the climate, to the weak soils and to the slope gradients
|
 |
a. The decrease of soil moisture (due to the delayed and reduced precipitation in autumn or the early dryness in spring) leads to a reduction in the grain yield and in the biomass and represents an important factor of crisis both for agriculture and livestock.
|
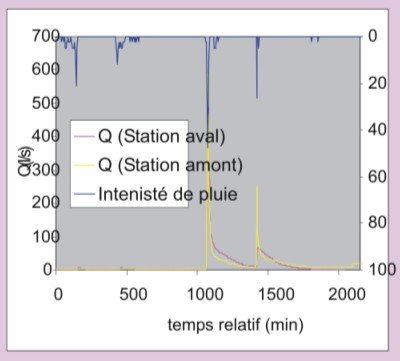 |
b. The concentration, in some years, of extreme events with heavy rain during autumn on land which is still completely bare, produce very important runoff and soil erosion
c. The decrease of the piezometric level, due to over- exploitation of wells and to the increase of runoff in the fields.
|
Potential strategies
Some new techniques introduced during the last decades of the 20th centruy by some farmers were identified by the stakeholders who participated in the field interviews and the workshop, as potential strategies for a water and soil conservation approach.
|
Cork Oak Forests
Assisted cork oak plantation as a strategy for the sustainability of the forest.
Expected impacts
- 5 x increase in soil humidity
- 2 x increase in percentage surface cover
- a reduction in soil compaction to half
- indicators of runoff to become rarely observed
- recovery of rare cork oak ecosystem species.
|
Degraded lands converted to pasture
The introduction of a fodder cultivation (lupin) in the crop rotation.
Expected impacts
- soil regeneration
- good plant cover of the soil, increased infiltration, reduced overland flow
- improved fodder yield
- improved income
Expected constraints
|
Rainfed annual agriculture
Rotation of annual cultivations.
Expected impacts
- farm diversification
- maintenance of soil fertility
- improved income
- food security
- diversification of nutrition
Expected constraints
- multiplicity of ploughing
- risk of erosion on soil prepared for spring cultivation
- high use of machinery
|
Rainfed cultivations associated with fruit tree plantations
Rainfed fruit tree poantations in lines separated by stripsof cereals or beans.
Expected impacts
- land protection
- improved income
- new methods and capacity building
- change of free grazing to intensive breeding
Expected constraints
- technical survey and maintenance
- cost of initial investment
- conflict with grazing which gives an immediate income
|
|













