Air temperature
Air temperature in combination with other climatic characteristics affects the xerothermic index and the vulnerability of an area for desertification. It is a critical environmental factor in determining water stress and transpiration of the growing vegetation as well as soil water evaporation and soil salinity and alkalinity. It is a critical factor affecting forest fires during the dry period in arid and semi-arid climatic conditions. Data on annual air temperature have been provided form the pertinent Meteorological Survives and for meteorological stations located in or nearby to the study sites areas. The following classes of air temperature (t) have been identified for the purpose of this project: (a) t<12 oC, (b) t changing from 12-15 oC, (c) t ranging from 15.1-18 oC, (d) t ranging from 18.1-21 oC, and (e) t >21 oC.
As Table 1 shows, air temperature has been defined in 446 questionnaires, corresponding to 8 study sites. This indicator was not filled in all the study sites, since it was identified as a candidate indicator affecting particularly areas sensitive to desertification due to soil salinization. Based on the available data for the above mentioned study sites, the average annual air temperature shows a wide range of values. As Fig. 2 shows, the dominant class of annual air temperature in the study field sites is less than 12 oC, covering 37.9% of the sites, and corresponding to all study field sites of Novij Saratov-Russia, and in several cases of Djanybek-Russia site. The next important class of air temperature defined is the range 15-18 oC, covering 30.7% of the study field sites, and corresponding to the study sites of Crete-Greece, Nestos-Greece, Cointzio catchment-Mexico, and Mação-Portugal. Annual air temperature ranging between 18-21 oC has been defined in 10.8% of the study field sites, corresponding to Crete-Greece study site. Annual air temperature >21 oC has been defined in 11.7% of the study field sites, corresponding to Boteti-Botswana, and Djanybek-Russia sites (Fig. 2). Finally, air temperature ranging between 12-15 oC has been found in 9% of the study field sites, corresponding to Cointzio catchment-Mexico, and Gois-Portugal study sites.
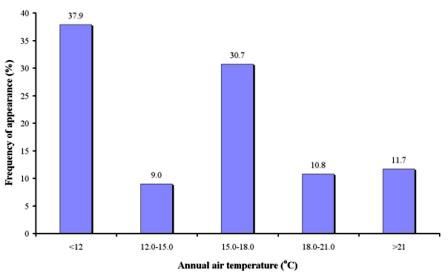
Fig. 2. Average annual air temperature classes prevailing in certain study field sites